Responsible Use of Antibiotics treatments,
Title: Responsible Use of Antibiotics in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction: The responsible use of antibiotics is a critical aspect of pediatric healthcare. In recent years, the overuse and misuse of antibiotics have led to the emergence of antibiotic-resistant bacteria, posing a significant threat to public health. This publication aims to provide an overview of the responsible use of antibiotics in children and adolescents, focusing on diagnosis, symptoms, and treatment options.
Understanding Antibiotic Resistance: Antibiotic resistance occurs when bacteria adapt and become resistant to the effects of antibiotics, rendering them ineffective. This issue arises from the inappropriate use of antibiotics, such as unnecessary prescriptions and incomplete treatment courses. Educating parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals about antibiotic resistance is crucial to promoting responsible antibiotic use.
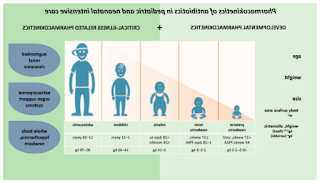
Common Infections in Children and Adolescents: Children and adolescents are susceptible to various bacterial and viral infections. Some common infections include:
a. Ear Infections (Otitis Media): Symptoms may include ear pain, fever, irritability, and fluid discharge from the ear. Most cases of otitis media are caused by viruses and do not require antibiotics. However, bacterial infections may necessitate antibiotic treatment.
b. Streptococcal Pharyngitis (Strep Throat): Symptoms include sore throat, fever, headache, and swollen tonsils. Accurate diagnosis through a throat swab is essential to differentiate between viral and bacterial causes. Antibiotics are prescribed for confirmed bacterial infections.
c. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): UTIs may present with symptoms such as frequent urination, pain or burning during urination, and abdominal pain. Laboratory tests, including urine culture, help identify the presence of bacteria. Appropriate antibiotic treatment is crucial to prevent complications.
- Diagnosis and Laboratory Tests: Accurate diagnosis is essential before initiating antibiotic therapy. The following diagnostic tools and laboratory tests aid in identifying bacterial infections:
a. Clinical Assessment: Thorough evaluation of symptoms, medical history, and physical examination assists in determining the likelihood of a bacterial infection.
b. Laboratory Tests: Various tests, including blood cultures, throat swabs, urine cultures, and stool cultures, help identify the causative bacteria and guide appropriate antibiotic selection.
- Symptoms and Red Flags: Recognizing symptoms that indicate the need for antibiotics is vital. However, it is equally crucial to identify symptoms that may not require antibiotic treatment, as overuse can contribute to antibiotic resistance. Some red flags that warrant prompt medical attention include:
a. High fever (above 38.5°C or 101.3°F) persisting for more than 48 hours. b. Severe pain or swelling that affects daily activities. c. Worsening or prolonged symptoms despite home remedies or over-the-counter medications. d. Signs of complications, such as difficulty breathing, dehydration, or rapid deterioration of overall health.
- Treatment Options and Antibiotic Stewardship: a. Non-antibiotic Treatments: Many childhood illnesses, such as the common cold and most cases of acute bronchitis, are caused by viral infections and do not require antibiotics. Supportive care, rest, fluids, and over-the-counter medications can help manage symptoms.
b. Antibiotic Therapy: When bacterial infections are diagnosed or strongly suspected, antibiotic therapy becomes necessary. Choosing the appropriate antibiotic based on the identified pathogen's susceptibility is crucial to ensure effective treatment and minimize resistance.
c. Antibiotic Stewardship: Healthcare professionals play a vital role in promoting responsible antibiotic use. Strategies such as education, guidelines, and surveillance programs can help reduce inappropriate antibiotic prescribing and encourage adherence to treatment guidelines.
Conclusion: The responsible use of antibiotics in children and adolescents is paramount to combat antibiotic resistance. Accurate diagnosis, appropriate treatment selection, and educating parents and healthcare professionals are essential components of promoting responsible antibiotic use. By adopting these measures, we can preserve the effectiveness of antibiotics and safeguard the health of future generations.

Post a Comment