Orchitis treatments, diagnosis and symptoms in
Title: Orchitis in Children and Adolescents: Understanding Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Introduction (100 words): Orchitis, a condition characterized by inflammation of the testicles, can affect individuals of all ages, including children and adolescents. Although relatively uncommon in this age group, it is essential to recognize the symptoms, diagnose the condition accurately, and provide appropriate treatment. This publication aims to provide a comprehensive overview of orchitis in children and adolescents, including its causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and available treatment options.
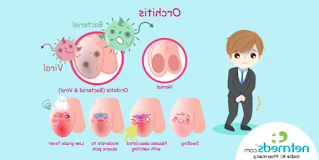
I. Understanding Orchitis (200 words): Orchitis refers to the inflammation of one or both testicles, often caused by viral or bacterial infections. In children and adolescents, the most common cause of orchitis is viral infection, primarily mumps, a contagious viral disease. Other viruses, such as the influenza virus or the Epstein-Barr virus, can also lead to orchitis. Bacterial orchitis, on the other hand, is typically the result of a urinary tract infection or sexually transmitted infection.
II. Recognizing Symptoms (300 words): The symptoms of orchitis in children and adolescents can vary, but commonly include:
- Testicular pain or discomfort
- Swelling and redness of the testicles
- Fever
- Nausea or vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- General malaise or fatigue
It is crucial for parents and caregivers to be vigilant about any changes in their child's behavior, particularly if they complain of pain or discomfort in the genital area. Prompt identification of symptoms can lead to early diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
III. Diagnosing Orchitis (300 words): To diagnose orchitis, healthcare professionals will evaluate the patient's medical history, conduct a physical examination, and perform additional tests if necessary. The physical examination may involve palpation of the testicles to assess tenderness, swelling, or irregularities. Laboratory tests, such as a complete blood count and urinalysis, may be ordered to rule out other potential causes and detect signs of infection.
In certain cases, ultrasound imaging may be used to visualize the testicles and assess their structure and blood flow. Ultrasound can help distinguish orchitis from other conditions, such as testicular torsion, which requires immediate surgical intervention.
IV. Treatment Options (400 words): The treatment approach for orchitis in children and adolescents typically involves addressing the underlying cause, managing symptoms, and preventing potential complications. The following treatment options may be considered:
Medications:
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help alleviate testicular pain and reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics: If the orchitis is caused by a bacterial infection, appropriate antibiotics will be prescribed to combat the infection.
Supportive Care:
- Rest and elevation: Encourage the child to rest and elevate the scrotum to alleviate swelling and discomfort.
- Applying cold compresses: Using cold packs or a clean cloth soaked in cold water can help reduce swelling and provide relief.
Prevention of Complications:
- If mumps is the cause of orchitis, ensuring that the child's mumps vaccination is up to date is crucial. MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine provides protection against mumps.
- Adequate hydration and pain management are essential to prevent dehydration and alleviate discomfort.
- Close monitoring for potential complications, such as abscess formation or testicular atrophy, may be required in severe cases.
Conclusion (100 words): Orchitis, though relatively uncommon in children and adolescents, requires timely recognition, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment. Understanding the symptoms and seeking medical attention promptly is vital to ensure effective management and prevent complications. Through prompt intervention, supportive care, and appropriate medication, children and adolescents with orchitis can experience relief from symptoms and achieve a full recovery. By spreading awareness about this condition, we can ensure better outcomes for affected individuals and contribute to their overall health and well-being.

Post a Comment