Laryngitis treatments, diagnosis and symptoms in
Title: Laryngitis in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatment Approaches
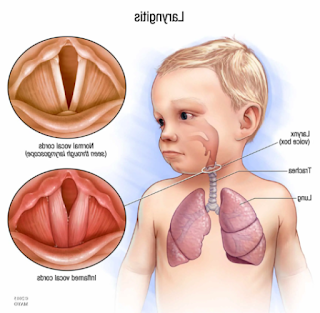
Introduction: Laryngitis is an inflammatory condition affecting the larynx, or the voice box, resulting in hoarseness or loss of voice. While laryngitis is commonly associated with adults, it can also affect children and adolescents. Recognizing the symptoms, obtaining an accurate diagnosis, and implementing appropriate treatments are essential for managing laryngitis in young individuals. This publication aims to provide a comprehensive overview of laryngitis in children and adolescents, including its causes, symptoms, diagnostic procedures, and various treatment approaches.
I. Causes and Risk Factors: Laryngitis in children and adolescents can be caused by various factors, including:
Viral Infections: The most common cause of laryngitis in children is viral infections, such as the common cold or flu. These viruses can directly infect the larynx and lead to inflammation.
Bacterial Infections: Less commonly, bacterial infections, such as streptococcus or staphylococcus, can cause laryngitis. Bacterial laryngitis often requires prompt medical attention.
Vocal Strain and Overuse: Children who frequently strain their voices, shout, or excessively use their vocal cords may develop laryngitis due to vocal abuse.
Allergies: Allergic reactions, particularly to environmental allergens like pollen or dust mites, can trigger laryngitis symptoms in susceptible individuals.
Reflux: Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can cause acid reflux into the throat, leading to laryngeal irritation and laryngitis.
II. Symptoms of Laryngitis in Children and Adolescents: Recognizing the signs and symptoms of laryngitis is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
Hoarseness or Voice Changes: Hoarseness is the hallmark symptom of laryngitis. Children and adolescents may experience a raspy, strained, or weak voice.
Sore Throat: Laryngitis can cause throat discomfort, pain, or a scratchy sensation, leading to difficulty swallowing or discomfort while speaking.
Dry Cough: A persistent, dry cough may develop as a result of laryngeal irritation.
Throat Clearing: Children with laryngitis may frequently clear their throats due to the sensation of mucus or irritation in the larynx.
Difficulty Speaking: In severe cases, laryngitis can lead to voice loss or complete loss of the ability to speak.
III. Diagnosis: Diagnosing laryngitis in children and adolescents involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms and a physical examination by a healthcare professional. The following diagnostic procedures may be employed:
Medical History: The doctor will inquire about the child's symptoms, duration, and possible triggers, such as recent illnesses or vocal strain.
Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the throat, vocal cords, and neck may be conducted to assess any visible signs of inflammation or other abnormalities.
Laboratory Tests: In some cases, the doctor may order blood tests or throat cultures to rule out bacterial infections or other underlying conditions.
Laryngoscopy: A laryngoscopy involves using a small camera or mirror to visualize the larynx directly. It helps in assessing the condition of the vocal cords and detecting any abnormalities.
IV. Treatment Approaches: The treatment of laryngitis in children and adolescents primarily focuses on relieving symptoms and addressing the underlying cause. The following approaches are commonly employed:
Voice Rest: Encouraging children to rest their voices and avoid activities that strain their vocal cords can help reduce laryngeal inflammation and promote healing.
Hydration: Adequate hydration helps maintain vocal cord health. Drinking plenty of fluids, preferably water, helps keep the throat moist and alleviates symptoms.
Humidification: Using a humidifier or inhaling steam can provide relief by moisturizing the airways and reducing throat irritation.
Medications: a) Analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, may help reduce pain and inflammation. b) Antibiotics: If bacterial infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the underlying cause. c) Antihistamines: In cases where allergies contribute to laryngitis, antihistamines can alleviate symptoms.
Voice Therapy: Referral to a speech-language pathologist specializing in voice therapy may be beneficial for individuals with recurrent laryngitis due to vocal misuse or abuse. Voice therapy focuses on proper vocal techniques and exercises to promote healthy voice production.
Treating Underlying Conditions: If laryngitis is secondary to an underlying condition, such as GERD, appropriate management of the underlying condition is crucial for effective laryngitis treatment.
Conclusion: Laryngitis in children and adolescents can be a distressing condition, impacting their ability to communicate and participate in daily activities. Early recognition of symptoms, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are essential for managing laryngitis effectively. By employing a combination of voice rest, hydration, medication, and addressing underlying causes, healthcare professionals can help young individuals recover from laryngitis and restore their vocal health, enabling them to resume their normal activities with confidence.

Post a Comment