Hepatitis A treatments, diagnosis and symptoms
Title: Hepatitis A in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatment
Introduction: Hepatitis A is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver and is caused by the Hepatitis A virus (HAV). While it can occur in individuals of all ages, children and adolescents are particularly susceptible to this highly contagious disease. This publication aims to provide comprehensive information on the diagnosis, symptoms, and treatment of Hepatitis A specifically in this age group. Understanding the unique challenges and considerations for children and adolescents can aid in timely detection, appropriate management, and prevention of further transmission.
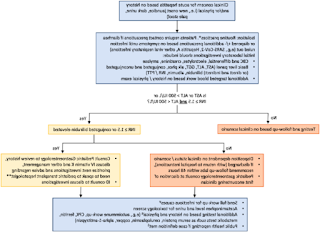
Diagnosis of Hepatitis A: Prompt and accurate diagnosis of Hepatitis A is essential for effective management. When a child or adolescent presents with symptoms suggestive of hepatitis, the healthcare provider will typically perform several diagnostic tests. These may include blood tests to measure liver function, detect specific antibodies, and identify the presence of the Hepatitis A virus. Serological tests, such as the detection of IgM antibodies against HAV, are particularly useful in confirming an acute infection. Additionally, a medical history review and physical examination can help in ruling out other potential causes of liver dysfunction.
Symptoms of Hepatitis A in Children and Adolescents: The incubation period of Hepatitis A ranges from two to six weeks, after which symptoms may start to appear. While some infected children and adolescents may remain asymptomatic, many experience a range of clinical manifestations. Common symptoms of Hepatitis A in this age group include fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes). Younger children may also exhibit non-specific symptoms such as fever, irritability, and diarrhea. It is important to note that the severity and duration of symptoms can vary greatly from child to child.
Treatment and Management: There is no specific antiviral treatment available for Hepatitis A. However, most cases in children and adolescents resolve on their own without complications. Supportive care aimed at alleviating symptoms and promoting liver recovery is the mainstay of treatment. Adequate rest, maintaining hydration, and ensuring a balanced diet are crucial. Alcohol and hepatotoxic medications should be avoided. Healthcare providers may recommend over-the-counter medications to relieve symptoms like fever and discomfort, but it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before administering any medication to a child.
Prevention and Vaccination: Prevention is key to reducing the incidence of Hepatitis A in children and adolescents. The most effective preventive measure is vaccination. The Hepatitis A vaccine is administered in two doses, typically given six months apart. It provides long-lasting immunity and is recommended for all children starting at the age of one year. Vaccination not only protects the individual but also helps in preventing the spread of the virus within communities.
In addition to vaccination, practicing good hygiene habits can significantly reduce the risk of transmission. Encouraging proper handwashing techniques, especially before meals and after using the toilet, is essential. Caregivers and educators should emphasize the importance of maintaining clean environments, particularly in settings where children gather, such as schools and daycare centers.
Conclusion: Hepatitis A is a contagious liver infection that can affect children and adolescents. Timely diagnosis, awareness of symptoms, and appropriate management play a crucial role in the well-being of affected individuals. While most cases resolve on their own without complications, supportive care is necessary to alleviate symptoms and ensure a full recovery. Vaccination and adherence to proper hygiene practices are vital for the prevention of Hepatitis A in this vulnerable population. By implementing preventive measures and providing accurate information, we can work towards reducing the burden of Hepatitis A among children and adolescents worldwide.

Post a Comment