Hepatitis B treatments, diagnosis and symptoms
Title: Hepatitis B in Children and Adolescents: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Strategies
Introduction (150 words): Hepatitis B is a viral infection that affects millions of people worldwide, including children and adolescents. Understanding the symptoms, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment strategies is crucial in managing this condition in younger individuals. This publication aims to provide a comprehensive overview of Hepatitis B in children and adolescents, shedding light on its symptoms, diagnostic methods, and available treatment options.
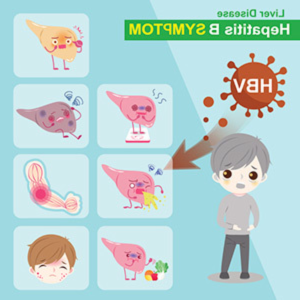
I. Symptoms of Hepatitis B in Children and Adolescents (300 words): Hepatitis B symptoms in children and adolescents can vary, and some individuals may exhibit no symptoms at all. The manifestation of symptoms can range from mild to severe and can include:
Fatigue and weakness: Children and adolescents with Hepatitis B may experience persistent fatigue and weakness, which can interfere with their daily activities and overall well-being.
Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes, known as jaundice, can occur in some cases of Hepatitis B. This is caused by the buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced by the liver.
Abdominal pain and discomfort: Hepatitis B can cause abdominal pain and discomfort, often accompanied by a loss of appetite, nausea, and vomiting.
Dark urine and pale stools: Hepatitis B may affect the liver's ability to process bilirubin, leading to dark-colored urine. Additionally, stools may appear pale or clay-colored.
Joint pain: Some children and adolescents may experience joint pain and stiffness as a result of the body's immune response to the Hepatitis B virus.
II. Diagnosis of Hepatitis B in Children and Adolescents (300 words): Accurate and timely diagnosis of Hepatitis B is crucial for appropriate management. The following diagnostic methods are commonly used:
Blood tests: Blood tests are performed to detect the presence of specific Hepatitis B antigens and antibodies, such as Hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and Hepatitis B core antibody (anti-HBc). These tests help confirm the infection and determine its stage.
Liver function tests: Liver function tests assess the liver's health by measuring various enzymes, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST). Elevated levels of these enzymes can indicate liver inflammation.
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR): PCR testing detects the genetic material of the Hepatitis B virus, providing further confirmation of the infection and determining the viral load.
Liver biopsy: In some cases, a liver biopsy may be recommended to assess the severity of liver damage caused by Hepatitis B. This involves obtaining a small sample of liver tissue for microscopic examination.
III. Treatment Strategies for Hepatitis B in Children and Adolescents (600 words): The management of Hepatitis B in children and adolescents aims to reduce liver inflammation, prevent complications, and suppress viral replication. The treatment strategies include:
Supportive care: Adequate rest, proper nutrition, and hydration are essential for children and adolescents with Hepatitis B. Avoiding alcohol and certain medications that can harm the liver is also crucial.
Antiviral medications: Antiviral drugs, such as entecavir and tenofovir, are commonly prescribed to suppress viral replication and reduce the risk of liver damage. The choice of medication depends on the child's age, viral load, and overall health.
Interferon therapy: Interferon-alpha therapy may be considered for certain cases, especially in older children and adolescents. This treatment stimulates the body's immune response to fight the Hepatitis B virus.
Vaccination: Hepatitis B vaccination is a preventive measure that can significantly reduce the risk of acquiring the infection. It is recommended for all infants and adolescents who haven't received it previously.
Regular monitoring: Children and adolescents with Hepatitis B require regular monitoring of liver function, viral load, and markers of liver fibrosis to assess the disease's progression and response to treatment.
Liver transplantation: In severe cases where the liver is extensively damaged, liver transplantation may be necessary. This option is considered when other treatments have failed or if the child develops complications such as liver cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conclusion (150 words): Hepatitis B is a significant health concern among children and adolescents globally. Recognizing the symptoms, ensuring accurate diagnosis, and implementing appropriate treatment strategies are vital for effective management. By providing comprehensive information on the symptoms, diagnostic methods, and available treatment options, this publication aims to enhance awareness and facilitate better healthcare delivery for children and adolescents affected by Hepatitis B. Early detection, timely intervention, and regular monitoring can help minimize liver damage, improve quality of life, and reduce the long-term complications associated with this viral infection.

Post a Comment