Foot fungus treatments, diagnosis and symptoms
Title: Foot Fungus in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Introduction (100 words): Foot fungus, also known as athlete's foot or tinea pedis, is a common fungal infection that can affect individuals of all ages, including children and adolescents. While it is not a life-threatening condition, it can cause discomfort and lead to complications if left untreated. This publication aims to provide a comprehensive overview of foot fungus, including its symptoms, diagnosis, and available treatment options specifically tailored for children and adolescents.
I. Understanding Foot Fungus (200 words): Foot fungus is caused by various types of fungi, most commonly Trichophyton and Epidermophyton. These fungi thrive in warm, moist environments, such as public swimming pools, locker rooms, and showers, making them highly contagious. Children and adolescents are particularly vulnerable due to their active lifestyles and increased exposure to these environments.
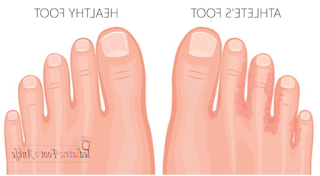
II. Symptoms of Foot Fungus (200 words): The symptoms of foot fungus in children and adolescents may vary but commonly include:
- Itching and burning sensation between the toes or on the soles of the feet.
- Peeling, cracking, or flaking skin.
- Redness, inflammation, and blisters.
- Unpleasant odor.
III. Diagnosis of Foot Fungus (200 words): Accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment. Healthcare professionals may perform the following assessments:
Physical Examination: The doctor examines the affected area, looking for characteristic signs of foot fungus, such as redness, scaling, and skin changes.
Microscopic Examination: A skin sample may be taken and examined under a microscope to identify the specific fungus responsible for the infection.
IV. Treatment Options (350 words): The treatment of foot fungus in children and adolescents typically involves a combination of self-care practices and medical interventions. It is important to consult a healthcare professional before starting any treatment. The following options are commonly recommended:
Topical Antifungal Medications: Over-the-counter antifungal creams, ointments, or powders containing active ingredients like clotrimazole, miconazole, or terbinafine can effectively treat mild cases of foot fungus. It is crucial to follow the recommended application instructions.
Oral Antifungal Medications: In more severe or persistent cases, oral antifungal medications may be prescribed. These medications are usually reserved for older children and adolescents and require close monitoring by a healthcare professional due to potential side effects.
Good Foot Hygiene: Encourage children and adolescents to practice proper foot hygiene, such as keeping their feet clean and dry, wearing clean socks made of breathable materials, and changing socks regularly.
Avoiding Contaminated Environments: Teach children to avoid walking barefoot in public areas and to wear protective footwear, such as shower shoes, in high-risk places.
Sterilizing Footwear: Fungal spores can reside in footwear, so it's essential to clean and disinfect shoes regularly to prevent reinfection.
Treating Concurrent Infections: If a foot fungus infection leads to secondary bacterial infections, such as cellulitis, the healthcare provider may prescribe antibiotics in addition to antifungal treatment.
V. Prevention Strategies (200 words): Prevention is key to reducing the risk of foot fungus in children and adolescents. Educate them about the following preventive measures:
Regularly washing and thoroughly drying the feet, paying special attention to the areas between the toes.
Avoiding sharing personal items like socks, shoes, towels, or nail clippers with others.
Encouraging the use of breathable footwear and changing socks frequently, especially after physical activities or when feet get wet.
Teaching good hygiene practices in public areas, such as avoiding walking barefoot and using personal protective footwear.
Conclusion (150 words): Foot fungus is a common fungal infection that affects children and adolescents. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and discomfort. By implementing proper foot hygiene practices, avoiding contaminated environments, and following preventive measures, the risk of foot fungus can be significantly reduced. If the infection persists or worsens, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for appropriate treatment options. Through a combination of self-care practices and medical interventions, foot fungus can be effectively managed, enabling children and adolescents to resume their regular activities without the burden of discomfort and potential complications.

Post a Comment