Epilepsy treatments, diagnosis and symptoms in
Title: Epilepsy in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Introduction (100 words): Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. It can affect individuals of all ages, including children and adolescents. Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and effective treatment are crucial in managing epilepsy in this vulnerable population. This publication aims to provide an in-depth understanding of epilepsy in children and adolescents, including its symptoms, diagnosis methods, and available treatment options. By raising awareness and promoting knowledge, we hope to improve the quality of life for young individuals living with epilepsy.
Symptoms of Epilepsy in Children and Adolescents (300 words): Recognizing the symptoms of epilepsy in children and adolescents is essential for early intervention and management. While seizures are the hallmark feature, it is important to note that epilepsy presents differently in each individual. Some common symptoms include:
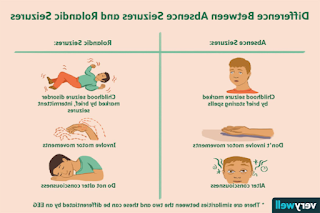
Generalized Seizures: These seizures involve both hemispheres of the brain and can manifest as tonic-clonic (grand mal), absence (petit mal), or atonic seizures. During tonic-clonic seizures, the child may experience muscle rigidity, convulsions, loss of consciousness, and urinary incontinence. Absence seizures are characterized by brief lapses of awareness, staring spells, and repetitive movements.
Focal Seizures: Focal seizures occur in specific areas of the brain and can be classified as focal onset aware or focal onset impaired awareness seizures. Symptoms depend on the affected brain region and may include repetitive movements, altered sensations, hallucinations, confusion, and loss of consciousness.
Other Signs: Children with epilepsy may also experience mood changes, sleep disturbances, difficulty concentrating, learning difficulties, and behavioral issues. It is crucial to consider these symptoms, as they can impact the child's overall well-being and academic performance.
Diagnosis of Epilepsy in Children and Adolescents (400 words): Accurate diagnosis is crucial to confirm epilepsy and determine the underlying cause. The diagnostic process typically involves the following:
Medical History and Physical Examination: A detailed medical history, including a description of the seizures, is obtained from the child and their caregivers. A thorough physical examination helps rule out other medical conditions that may cause similar symptoms.
Electroencephalogram (EEG): EEG is a non-invasive test that records electrical activity in the brain. It can detect abnormal brain waves during seizures or interictal periods, aiding in the diagnosis and classification of epilepsy.
Neuroimaging: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are often performed to identify any structural abnormalities in the brain that may be causing seizures. This imaging technique helps determine the precise location and extent of the abnormality.
Blood Tests: Blood tests are conducted to screen for any metabolic or genetic conditions that could be contributing to epilepsy symptoms. These tests help identify underlying causes and guide treatment decisions.
Video EEG Monitoring: In some cases, a prolonged video EEG monitoring is required, especially when the diagnosis is uncertain. This allows for the correlation of clinical events with EEG findings, increasing diagnostic accuracy.
Treatment Options for Epilepsy in Children and Adolescents (500 words): The treatment of epilepsy in children and adolescents aims to reduce or eliminate seizures while minimizing side effects and improving overall quality of life. The choice of treatment depends on various factors, including the child's age, seizure type, frequency, and underlying cause. The following treatment options are commonly utilized:
Antiepileptic Drugs (AEDs): AEDs are the primary treatment for epilepsy. Several medications are available, and the choice depends on the type of seizures and the child's individual needs. Regular monitoring is necessary to adjust dosage and assess any side effects.
Ketogenic Diet: The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate, and adequate-protein diet that has shown efficacy in reducing seizures, particularly in children with medication-resistant epilepsy. It requires careful supervision by a healthcare professional and strict adherence.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): VNS is a non-pharmacological treatment option that involves implanting a device under the skin of the chest. The device sends electrical impulses to the vagus nerve, which then modulates brain activity and helps reduce seizure frequency.
Responsive Neurostimulation (RNS): RNS is a newer treatment modality that involves implanting a neurostimulator device directly into the brain. The device monitors brain activity and delivers targeted electrical stimulation to prevent seizure onset.
Epilepsy Surgery: For children with drug-resistant epilepsy and identified focal brain abnormalities, surgical intervention may be considered. The goal of surgery is to remove or disconnect the seizure focus while preserving brain function.
Conclusion (100 words): Epilepsy can significantly impact the lives of children and adolescents, but with proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment, its impact can be minimized. By recognizing the symptoms, conducting thorough diagnostic evaluations, and implementing tailored treatment plans, healthcare professionals can effectively manage epilepsy in this population. Ongoing research and advancements in treatment options continue to provide hope for better outcomes and improved quality of life for children and adolescents living with epilepsy. By raising awareness and promoting early intervention, we can create a supportive environment that empowers young individuals with epilepsy to lead fulfilling lives.

Post a Comment