Ankle sprain treatments, diagnosis and symptoms
Title: Ankle Sprain in Children and Adolescents: Diagnosis, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Introduction:
Ankle sprains are a common injury in children and adolescents, often resulting from sports activities, recreational play, or accidents. While ankle sprains may seem like a minor injury, they can cause significant discomfort, mobility limitations, and potential long-term complications if not properly diagnosed and treated. This publication aims to provide a comprehensive overview of ankle sprains in children and adolescents, including information on diagnosis, symptoms, and treatment options.
I. Understanding Ankle Sprains:
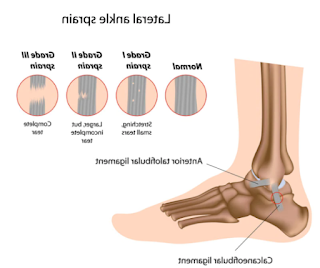
Definition: An ankle sprain occurs when the ligaments surrounding the ankle joint are stretched or torn, typically due to excessive twisting or rolling of the ankle.
Causes: Common causes of ankle sprains in children and adolescents include sports activities such as soccer, basketball, and gymnastics, as well as accidents during play or falls from heights.
II. Diagnosis of Ankle Sprains:
Medical Evaluation: When a child or adolescent presents with symptoms of an ankle sprain, a medical professional will conduct a thorough physical examination to assess the extent of the injury.
Imaging Tests: Imaging tests, such as X-rays, may be ordered to rule out fractures or other bone-related injuries.
III. Symptoms of Ankle Sprains:
Pain and Swelling: Children and adolescents with ankle sprains commonly experience pain and swelling around the affected ankle. The severity of pain may vary depending on the extent of the injury.
Bruising: Bruising or discoloration around the ankle area is another common symptom.
Difficulty Walking or Bearing Weight: Ankle sprains can make it challenging for children and adolescents to walk or bear weight on the affected foot.
IV. Treatment Options:
R.I.C.E Method: The R.I.C.E method, which stands for rest, ice, compression, and elevation, is often the initial approach to managing ankle sprains. It helps reduce pain and swelling and promotes healing.
Immobilization: In some cases, a medical professional may recommend immobilizing the ankle using a brace, splint, or cast to facilitate healing and protect the injured ligaments.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy plays a crucial role in ankle sprain recovery. It helps restore strength, flexibility, and stability to the ankle joint, reducing the risk of reinjury.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may be recommended to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation.
Surgical Intervention: Surgery is rarely required for ankle sprains in children and adolescents. It is typically reserved for severe cases or instances where conservative treatments fail.
V. Prevention and Rehabilitation:
Preventive Measures: Educating children, parents, and coaches about proper warm-up exercises, wearing appropriate footwear, and practicing safe techniques can help reduce the risk of ankle sprains.
Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation after an ankle sprain involves a gradual return to physical activities, under the guidance of a healthcare professional, to ensure optimal healing and prevent reinjury.
Conclusion:
Ankle sprains are a common injury among children and adolescents, with the potential for significant discomfort and limitations in daily activities. Prompt and accurate diagnosis, along with appropriate treatment, is essential to ensure proper healing and prevent long-term complications. By following preventive measures and engaging in rehabilitation exercises, children and adolescents can minimize the risk of future ankle sprains. If you suspect an ankle sprain in your child or adolescent, seeking medical attention is crucial to receive the appropriate diagnosis and treatment for their speedy recovery.

Post a Comment